Adresse
304, rue Cardinal Nord
Centre Dorchester, MA 02124
Heures de travail
Du lundi au vendredi : 7h - 19h
Week-end : 10h - 17h
Adresse
304, rue Cardinal Nord
Centre Dorchester, MA 02124
Heures de travail
Du lundi au vendredi : 7h - 19h
Week-end : 10h - 17h
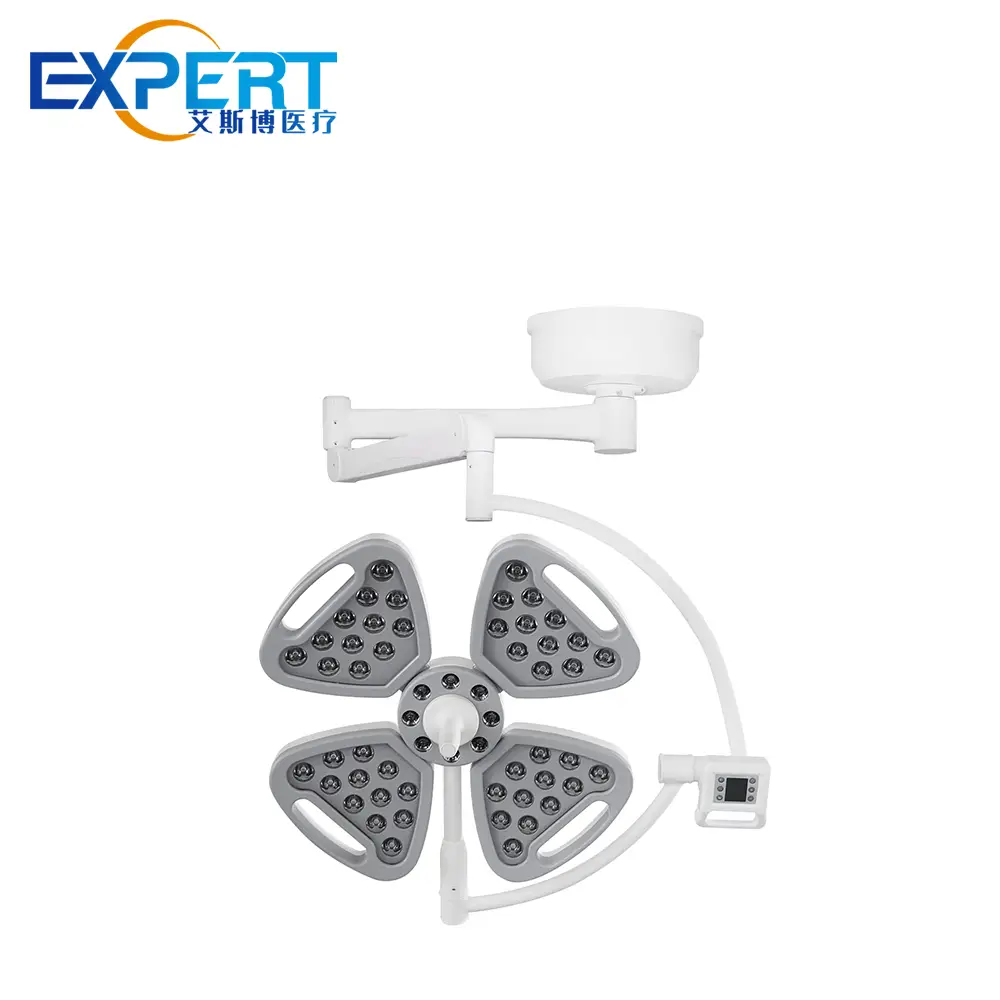

This comprehensive guide delves into the various surgical lights uses, exploring their features, types, and significance in modern surgical practice.
Bienvenue sur mon blog !
Avant de plonger dans le contenu, j'aimerais que vous me rejoigniez sur mes plateformes de médias sociaux où je partage plus d'informations, interagis avec la communauté et publie des mises à jour. Voici comment vous pouvez me contacter :
Facebook :https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=100071234835011
LinkedIn :https://www.linkedin.com/company/74943205/admin/dashboard/
YouTube :www.youtube.com/@shandongexpertmedicalequip4695
TikTok :www.tiktok.com/@expertmedical
Commençons maintenant notre voyage ensemble. J'espère que vous trouverez le contenu ici instructif, engageant et utile.

Surgical lights are indispensable tools in the operating room (OR), providing crucial illumination for surgeons and their teams to perform intricate procedures with precision and confidence. These specialized lights go beyond simple illumination, offering adjustable intensity, focus, and color temperature to optimize visibility and minimize eye strain during surgery. This comprehensive guide delves into the various surgical lights uses, exploring their features, types, and significance in modern surgical practice.
Surgical lights play a pivotal role in ensuring successful surgical outcomes. Adequate lighting is essential for:


Surgical lights come in various types, each designed to meet specific surgical needs:
Modern surgical lights boast a range of features to enhance their functionality and usability:
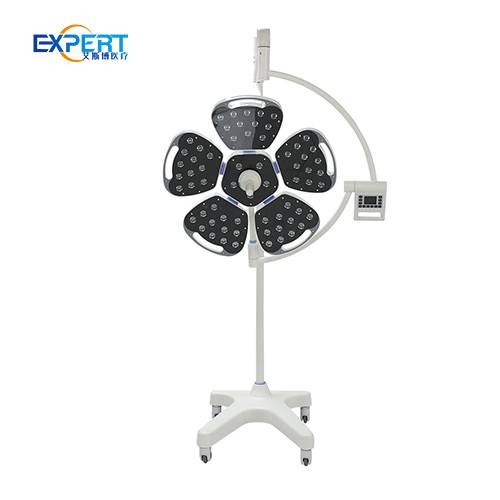
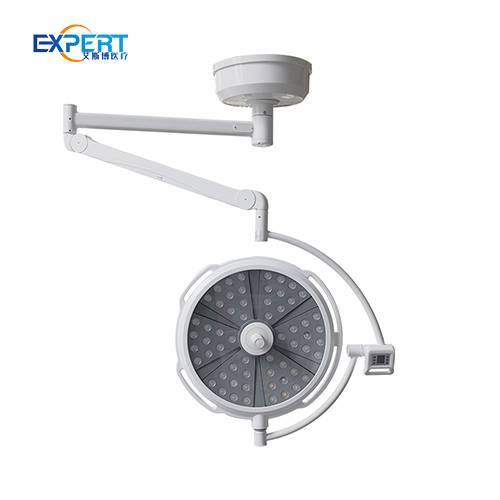
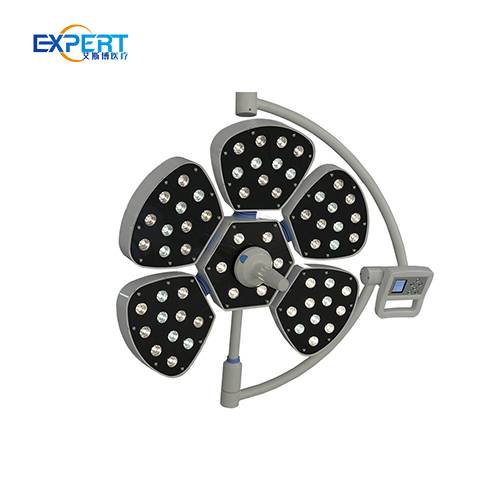
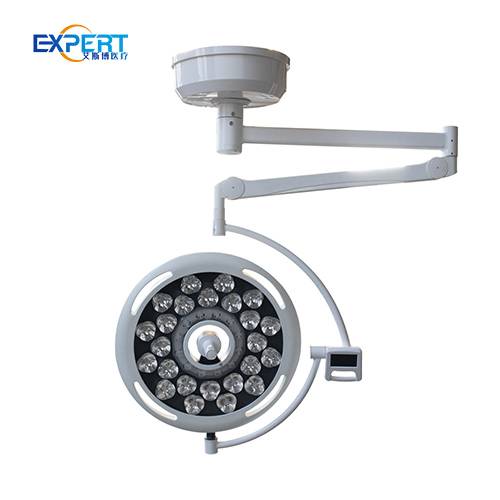
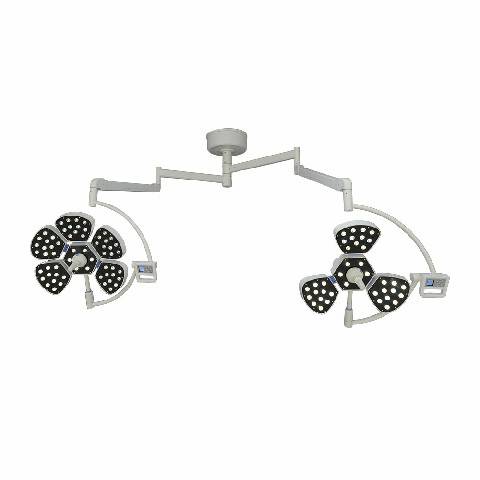
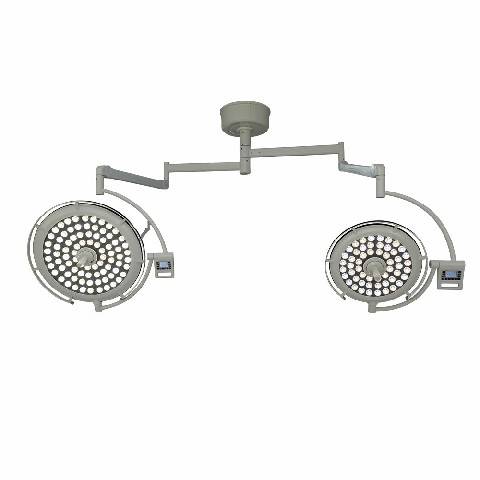
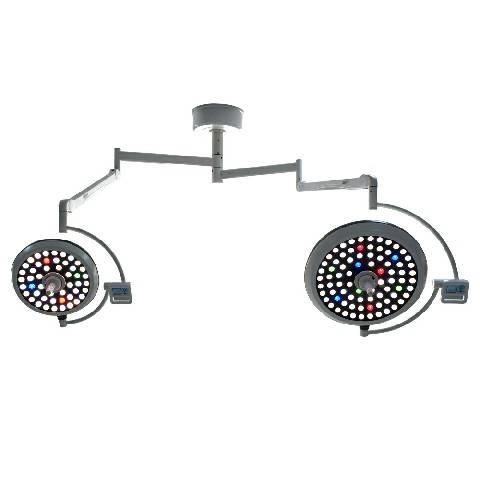
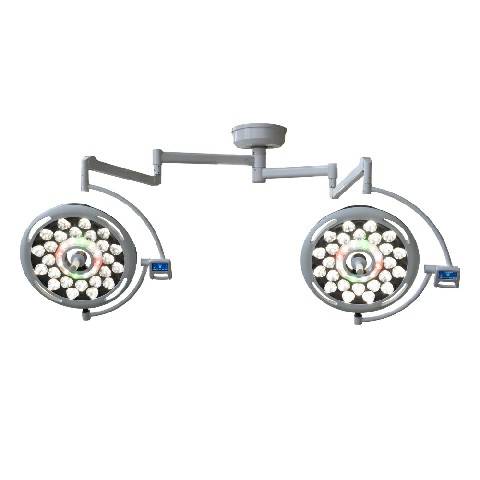








Surgical lights are essential in a wide range of surgical procedures, including:
| Caractéristique | Ceiling-mounted Surgical Lights | Lampes chirurgicales mobiles | Lampes chirurgicales à LED | Lampes chirurgicales halogènes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positionnement | Fixed, adjustable | Portable, flexible | Fixed, adjustable | Fixed, adjustable |
| Mobilité | Limité | Haut | Limité | Limité |
| Qualité de la lumière | Excellent | Bien | Excellent | Bien |
| Efficacité énergétique | Haut | Haut | Haut | Modéré |
| Durée de vie | Long | Long | Long | Plus court |
| Production de chaleur | Faible | Faible | Faible | Modéré |
| Coût | Plus haut | Modéré | Plus haut | Inférieur |
| Common Uses | Major surgeries | Minor procedures, emergency situations | All types of surgeries | Some surgeries, less common |
Proper maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of surgical lights:

Surgical lighting technology continues to evolve, with ongoing advancements aimed at improving visualization, reducing eye strain, and enhancing surgical outcomes. Future trends include:
Éclairages chirurgicaux are indispensable tools in the OR, providing crucial illumination for surgeons to perform procedures with precision and confidence. Understanding the various surgical lights uses, their features, and their importance in different procedures is essential for ensuring optimal surgical outcomes and patient safety. As technology continues to advance, surgical lighting will play an even greater role in shaping the future of surgical care.
Q : À quelle fréquence faut-il éclairages chirurgicaux être nettoyé?
A: Surgical lights should be cleaned regularly, ideally after each procedure, to maintain optimal performance and prevent contamination.
Q: Can surgical lights be adjusted during surgery?
A: Yes, most surgical lights are equipped with sterile handles that allow surgeons or surgical assistants to adjust the light position and intensity during a procedure.
Q: What is the importance of color temperature in éclairage chirurgical?
A: Color temperature affects how colors appear under the light. Adjustable color temperature allows surgeons to choose the optimal lighting for different tissues and procedures, reducing eye strain and improving visualization.