Adresse
304, rue Cardinal Nord
Centre Dorchester, MA 02124
Heures de travail
Du lundi au vendredi : 7h - 19h
Week-end : 10h - 17h
Bienvenue sur mon blog !
Avant de plonger dans le contenu, si vous êtes intéressé par nos produits ou si vous avez des questions, n'hésitez pas à visiter notre Nous contacter sur notre site web. Notre équipe est à votre disposition pour répondre à vos questions, passer vos commandes ou vous apporter toute l'assistance dont vous pourriez avoir besoin.
Commençons maintenant notre voyage ensemble. J'espère que vous trouverez ce contenu instructif, captivant et utile.
Les éclairages chirurgicaux sont un élément essentiel de tout bloc opératoire. Ils fournissent l'éclairage nécessaire aux chirurgiens pour réaliser des interventions avec précision et sécurité. Grâce aux progrès technologiques, différents types d'éclairages chirurgicaux ont été développés, chacun offrant des caractéristiques et des avantages uniques. Ce guide complet explore les différents types d'éclairages chirurgicaux, leurs applications et vous aide à choisir la meilleure option pour votre cabinet médical. En comprenant les caractéristiques clés de chaque type, vous pourrez prendre une décision éclairée et améliorer la qualité des soins prodigués aux patients.
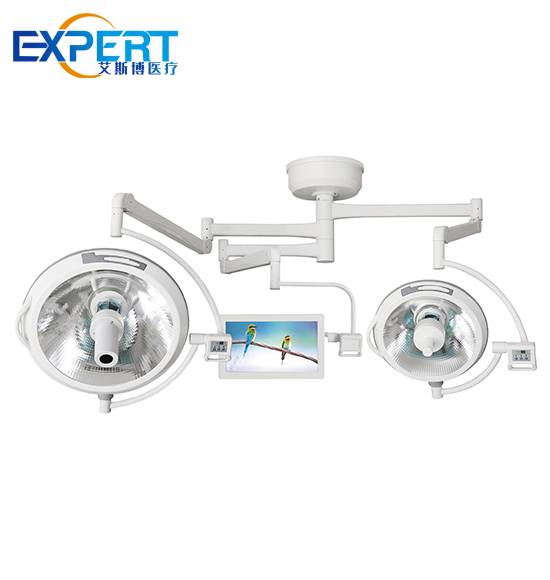

Les éclairages chirurgicaux jouent un rôle essentiel pour garantir aux chirurgiens une vision claire et dégagée du site opératoire. Un éclairage adéquat réduit les risques d'erreur, améliore la précision visuelle et optimise les résultats chirurgicaux. Un éclairage chirurgical adapté peut également réduire la fatigue oculaire du personnel médical, lui permettant ainsi de travailler plus confortablement et plus efficacement.
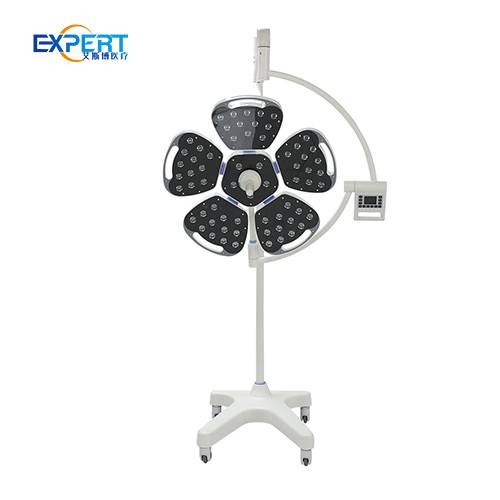
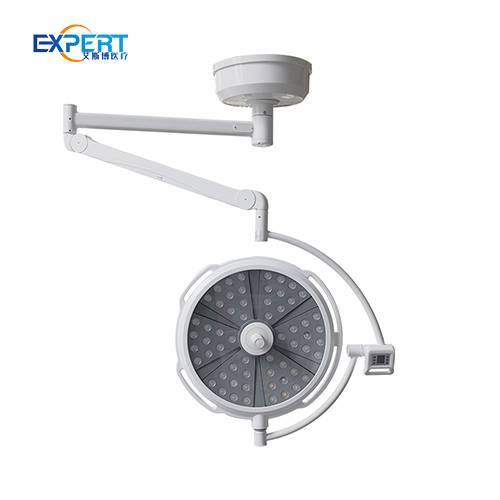
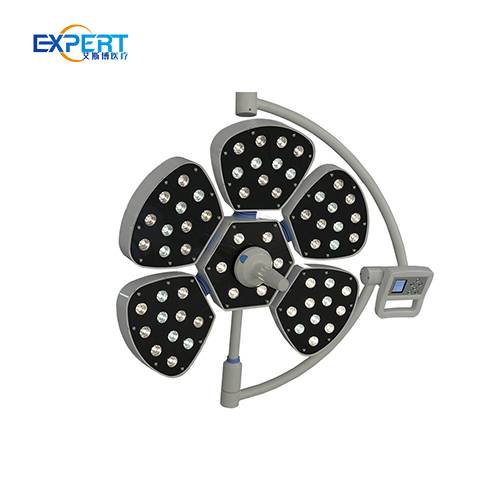
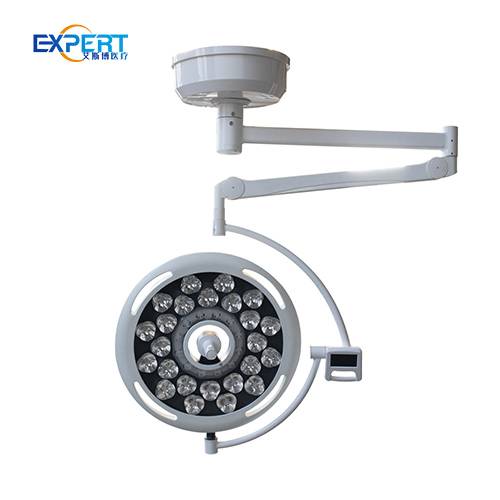
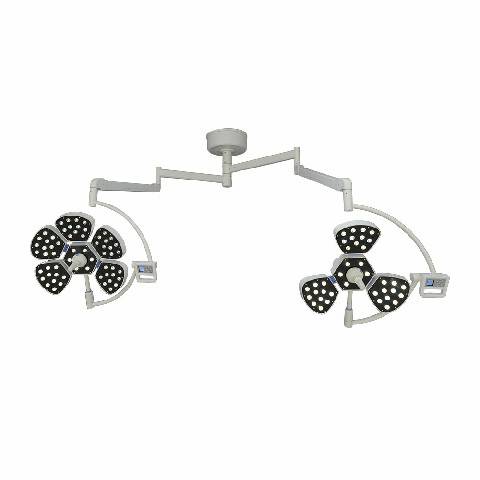
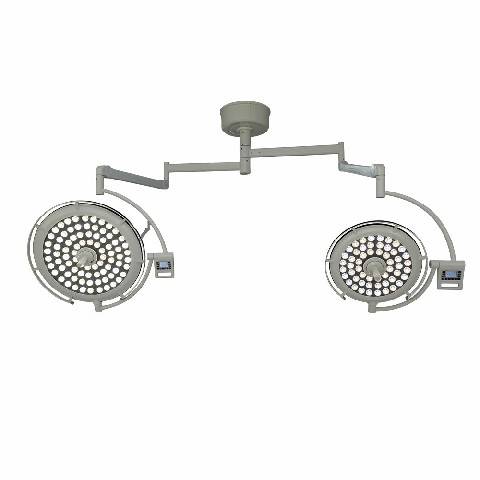
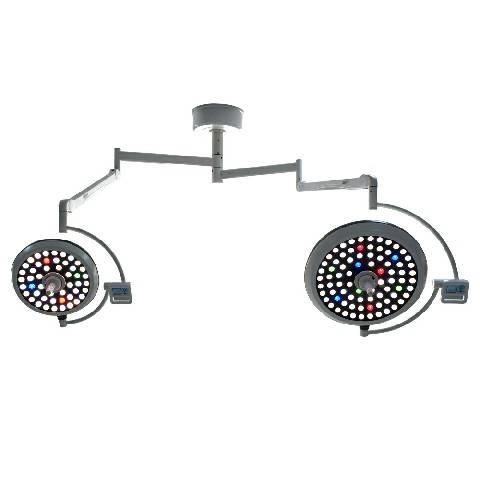
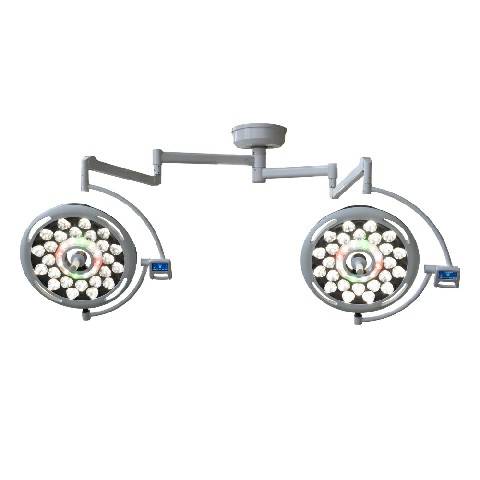
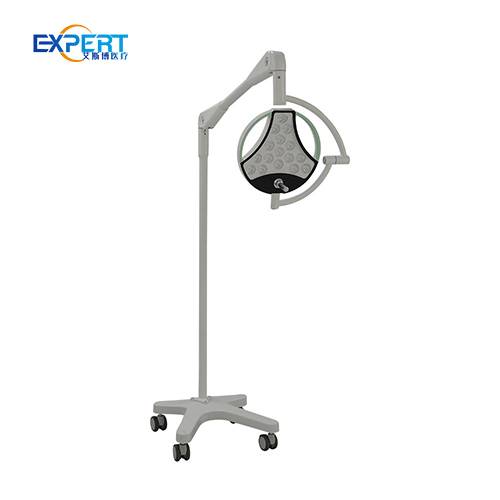








Les éclairages chirurgicaux à LED (diodes électroluminescentes) comptent parmi les plus populaires en raison de leur efficacité énergétique, de leur longue durée de vie et de leur qualité d'éclairage supérieure. Ils produisent un éclairage intense et constant avec une émission de chaleur minimale.
Les éclairages chirurgicaux à LED conviennent à diverses interventions chirurgicales, des interventions mineures aux interventions complexes. Ils sont parfaits pour les environnements où un éclairage constant et de haute qualité est essentiel.
Les éclairages chirurgicaux halogènes sont incontournables dans les blocs opératoires depuis de nombreuses années. Ils utilisent du gaz halogène pour augmenter le rendement lumineux et l'efficacité, offrant un éclairage intense et ciblé.
Les éclairages chirurgicaux halogènes sont couramment utilisés dans divers contextes chirurgicaux, notamment en consultation externe et en milieu hospitalier. Ils sont particulièrement utiles pour les interventions nécessitant un éclairage intense et ciblé.
Les éclairages chirurgicaux au xénon utilisent du gaz xénon pour produire une lumière blanche et brillante, proche de la lumière naturelle. Ce type d'éclairage offre un excellent rendu des couleurs et un minimum d'ombres.
Les éclairages chirurgicaux au xénon sont souvent utilisés dans les blocs opératoires nécessitant une lumière intense et naturelle. Ils sont idéaux pour les interventions chirurgicales impliquant des tissus délicats et des mouvements précis.
Les éclairages chirurgicaux fluorescents utilisent des ampoules fluorescentes pour fournir un éclairage large et uniforme. Ces éclairages sont réputés pour leur efficacité énergétique et leur faible dégagement de chaleur.
Les éclairages chirurgicaux fluorescents conviennent aux interventions chirurgicales générales et aux environnements nécessitant un éclairage large et diffus. Ils sont souvent utilisés dans les salles d'examen et les blocs opératoires de petite chirurgie.
Les éclairages chirurgicaux portables sont conçus pour être flexibles et mobiles. Faciles à déplacer et à ajuster, ils sont parfaits pour une utilisation dans plusieurs endroits ou en situation d'urgence.
Les éclairages chirurgicaux portables sont couramment utilisés dans les hôpitaux de campagne, les centres de chirurgie ambulatoire et les interventions d'urgence. Ils fournissent un éclairage essentiel lorsque les éclairages chirurgicaux fixes ne sont pas disponibles.
| Type de lampe chirurgicale | Luminosité (Lux) | Durée de vie (heures) | Émission de chaleur | Efficacité énergétique | Coût | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIRIGÉ | Jusqu'à 160 000 | 50,000+ | Faible | Haut | Modéré-élevé | Chirurgie générale, interventions complexes |
| Halogène | Jusqu'à 120 000 | 2,000-3,000 | Haut | Modéré | Faible-Modéré | Cliniques externes, procédures détaillées |
| Xénon | Jusqu'à 200 000 | 1,000-2,000 | Modéré | Faible | Haut | Chirurgies de haute précision, travail délicat des tissus |
| Fluorescent | Jusqu'à 100 000 | 7,000-10,000 | Faible | Haut | Modéré | Chirurgie générale, salles d'examen |
| Portable | Variable | Variable | Variable | Variable | Modéré | Hôpitaux de campagne, intervention d'urgence |
Les éclairages chirurgicaux à LED offrent une efficacité énergétique supérieure et une durée de vie plus longue que les éclairages halogènes. Ils produisent moins de chaleur et offrent une intensité réglable, ce qui les rend adaptés à un large éventail d'interventions. En revanche, les éclairages halogènes sont généralement moins chers et offrent un éclairage intense et ciblé, que certains chirurgiens privilégient pour des tâches spécifiques.
Les éclairages chirurgicaux au xénon offrent un éclairage comparable à la lumière du jour avec un excellent rendu des couleurs, ce qui les rend idéaux pour les interventions chirurgicales de haute précision. Cependant, ils sont plus chers et ont une durée de vie plus courte que les éclairages fluorescents. Les éclairages chirurgicaux fluorescents offrent un éclairage uniforme et diffus avec une faible émission de chaleur, ce qui les rend adaptés aux interventions chirurgicales générales et aux salles d'examen.
Lors du choix d'un éclairage opératoire, tenez compte des exigences spécifiques de votre cabinet. Évaluez des facteurs tels que la luminosité, le rendu des couleurs, l'émission de chaleur, l'efficacité énergétique et le coût. Le tableau ci-dessus compare différents types d'éclairages opératoires et vous aide à prendre une décision éclairée en fonction de vos besoins.

Pour garantir des performances et une longévité optimales, nettoyez régulièrement les éclairages chirurgicaux conformément aux instructions du fabricant. Utilisez des produits de nettoyage non abrasifs et des chiffons doux pour éviter d'endommager les surfaces des éclairages.
Pour les éclairages chirurgicaux utilisant des ampoules, comme les lampes halogènes et au xénon, remplacez-les au besoin pour maintenir la luminosité et la clarté. Suivez les instructions du fabricant pour le remplacement des ampoules afin de garantir un fonctionnement sûr et efficace.
Inspectez régulièrement les éclairages chirurgicaux pour détecter tout signe d'usure ou de dommage. Planifiez un entretien régulier avec un technicien qualifié pour résoudre tout problème et garantir le bon fonctionnement des éclairages.
Choisir le bon éclairage opératoire est essentielle pour garantir une visibilité et des performances optimales lors des interventions chirurgicales. Comprendre les différents types d'éclairages chirurgicaux et leurs caractéristiques uniques vous permettra de prendre une décision éclairée et d'améliorer la qualité des soins dans votre cabinet médical. Que vous optiez pour un éclairage chirurgical LED, halogène, xénon, fluorescent ou portable, tenez compte des besoins spécifiques de votre cabinet et des avantages de chaque type. Avec un éclairage chirurgical adapté, vous pouvez améliorer les résultats chirurgicaux, réduire les risques d'erreur et créer un environnement de travail confortable pour votre personnel médical.
Les principaux types d'éclairages chirurgicaux comprennent les éclairages LED, halogènes, au xénon, fluorescents et portables. Chaque type offre des caractéristiques et des avantages uniques, les rendant adaptés à différentes applications chirurgicales.
Les éclairages chirurgicaux à LED sont plus économes en énergie, ont une durée de vie plus longue et produisent moins de chaleur que les éclairages halogènes. Leur intensité est réglable et convient à un large éventail d'interventions. Les éclairages halogènes, bien que moins coûteux, offrent un éclairage intense et ciblé, idéal pour certaines tâches.
Lors du choix d'un éclairage opératoire, tenez compte de facteurs tels que la luminosité, le rendu des couleurs, l'émission de chaleur, l'efficacité énergétique, le coût et les exigences spécifiques de l'application. Évaluez les avantages et les inconvénients de chaque type d'éclairage afin de sélectionner la solution la plus adaptée à votre pratique.
Les éclairages chirurgicaux doivent être entretenus régulièrement conformément aux recommandations du fabricant. Des inspections, des nettoyages et des remplacements d'ampoules réguliers contribuent à maintenir des performances optimales et à prolonger la durée de vie des éclairages.
Les éclairages chirurgicaux portables sont polyvalents et peuvent être utilisés pour diverses interventions, notamment dans les hôpitaux de campagne et les situations d'urgence. Cependant, pour les interventions chirurgicales complexes et de haute précision, des éclairages chirurgicaux fixes dotés de fonctionnalités avancées peuvent être plus adaptés.
