Endereço
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Horas de trabalho
Segunda a sexta: 7h00 - 19h00
Fim de semana: 10h - 17h
Bem-vindo ao meu blog!
Antes de mergulharmos no conteúdo, adoraria que você se juntasse a mim nas minhas plataformas de mídia social, onde compartilho mais insights, interajo com a comunidade e posto atualizações. Veja como você pode se conectar comigo:
Facebook:https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=100071234835011
LinkedIn:https://www.linkedin.com/company/74943205/admin/dashboard/
YouTube:www.youtube.com/@shandongexpertmedicalequip4695
TikTok:www.tiktok.com/@expertmedical
Agora, vamos começar nossa jornada juntos. Espero que você ache o conteúdo aqui perspicaz, envolvente e valioso.
No reino da medicina moderna, as luzes cirúrgicas desempenham um papel fundamental para garantir visibilidade e precisão ideais durante procedimentos cirúrgicos. Das luzes halógenas tradicionais aos sistemas avançados de LED, a evolução da tecnologia de iluminação cirúrgica revolucionou o ambiente da sala de cirurgia. Neste guia abrangente, nos aprofundamos nos principais aspectos das luzes cirúrgicas, sua importância em ambientes cirúrgicos e os últimos avanços que moldam o campo.

Luzes cirúrgicas são sistemas de iluminação especializados projetados para fornecer iluminação brilhante e sem sombras do campo cirúrgico. Elas são estrategicamente posicionadas acima da mesa de operação para iluminar o local cirúrgico, minimizando o brilho e as sombras. Abaixo está uma tabela comparando diferentes tipos de luzes cirúrgicas com base em parâmetros-chave:
| Tipo | Fonte de luz | Temperatura de cor | Intensidade (Lux) | Tempo de vida (horas) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Halogênio | Lâmpada halógena | 3.500 – 4.500 mil | 30,000 – 60,000 | 1,000 – 2,000 |
| LIDERADO | Diodo emissor de luz | 4.500 – 5.500 mil | 60,000 – 160,000 | 30,000 – 60,000 |
| Xenônio | Lâmpada Xenon | 5.000 – 6.000 mil | 100,000 – 160,000 | 1,000 – 2,000 |
As luzes cirúrgicas são avaliadas com base em várias características cruciais que determinam sua eficácia e adequação para diversas aplicações cirúrgicas:
Luzes cirúrgicas são indispensáveis em uma ampla gama de especialidades médicas, incluindo:
Cirurgia geral: Fornecendo iluminação clara e consistente do campo cirúrgico para diversos procedimentos, como apendicectomias, reparos de hérnia e cirurgias laparoscópicas. A iluminação garante visibilidade ideal durante toda a operação.
Cirurgia ortopédica: Facilitando a visualização precisa e detalhada durante substituições complexas de articulações, reparos de fraturas e cirurgias de coluna. Uma iluminação precisa é essencial para resultados bem-sucedidos nesses procedimentos complexos.
Neurocirurgia: Garantir iluminação ideal e focada para procedimentos altamente delicados que envolvem o cérebro e a medula espinhal, como ressecções de tumores e reparos de aneurismas. A precisão da iluminação pode impactar significativamente o sucesso dessas operações críticas.
Cirurgia plástica: Aumentando a visibilidade e a precisão de procedimentos meticulosos, como reconstruções faciais, aumentos de mama e cirurgias estéticas que exigem o mais alto nível de precisão e atenção aos detalhes.
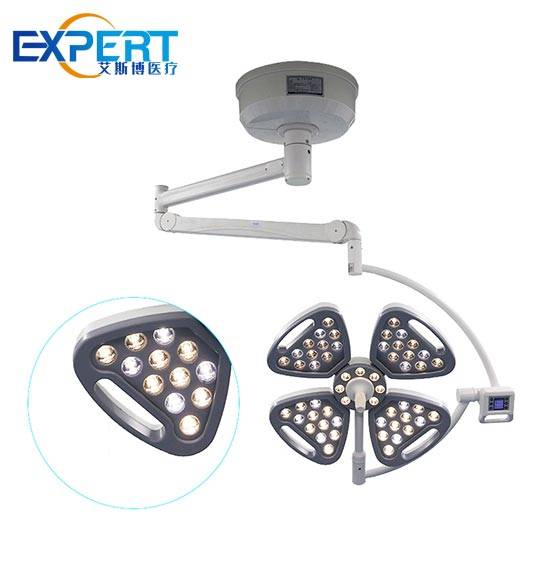
Escolha do procedimento cirúrgico adequado luzes envolve uma consideração cuidadosa de vários fatores:
Luzes cirúrgicas são ferramentas indispensáveis em salas de cirurgia modernas, fornecendo aos cirurgiões a iluminação necessária para realizar procedimentos complexos com segurança e eficácia. De luzes halógenas tradicionais a sistemas avançados de LED, a evolução da tecnologia de iluminação cirúrgica continua a impulsionar melhorias nos resultados dos pacientes e na eficiência cirúrgica. Ao entender os principais recursos e vantagens de diferentes tipos de luzes cirúrgicas, as instalações de saúde podem tomar decisões informadas para aprimorar a experiência cirúrgica para pacientes e equipe médica.
P: As luzes cirúrgicas de LED são adequadas para todos os tipos de cirurgias?
R: Sim, as luzes cirúrgicas de LED são versáteis e podem ser usadas em várias especialidades cirúrgicas. No entanto, é essencial garantir que o modelo de luz específico atenda aos requisitos do procedimento que está sendo realizado.
P: Como escolher a luz cirúrgica certa para minha sala de cirurgia?
R: Ao selecionar luzes cirúrgicas, considere fatores como intensidade da luz, reprodução de cores, ajustabilidade e compatibilidade com o layout e o equipamento da sala de cirurgia.
P: As luzes cirúrgicas podem ser esterilizadas entre os procedimentos?
R: Dependendo do design, algumas luzes cirúrgicas apresentam alças ou tampas removíveis e autoclaváveis que permitem fácil esterilização. É crucial seguir as recomendações do fabricante para procedimentos de limpeza e esterilização.
P: As luzes cirúrgicas podem ser esterilizadas entre os procedimentos?
R: Dependendo do design, algumas luzes cirúrgicas apresentam alças ou tampas removíveis e autoclaváveis que permitem fácil esterilização. É crucial seguir as recomendações do fabricante para procedimentos de limpeza e esterilização.
P: Quais são os requisitos de manutenção para luzes cirúrgicas?
R: As tarefas de manutenção de rotina para luzes cirúrgicas podem incluir substituição de lâmpadas, limpeza de lentes e refletores e inspeção periódica para detectar quaisquer sinais de danos ou mau funcionamento.
