Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Proper illumination in the operating room is vital for surgeons to be able to clearly see the surgical site and patient anatomy. Surgical lights, also known as operating lights or surgical luminaires, provide focused and intense light over the surgical area. There are several types of surgical lights designed for different needs and preferences. When choosing surgical lights for the OR, factors like intensity, light temperature, adjustability, and shadow reduction need to be considered.
In this blog post, we will discuss the different types of surgical lights available and their key features. We will look at traditional ceiling-mounted surgical lights as well as new innovative designs like LED lights and flat panel lights.

There are two main configurations of surgical lights:
Some key types within these configurations include:
Halogen bulbs have been traditionally used in surgical lighting. Features include:
However, halogen lights have some downsides such as high heat emission and short bulb life of 2,000 hours. They are being replaced in many ORs by LED and other newer technologies.
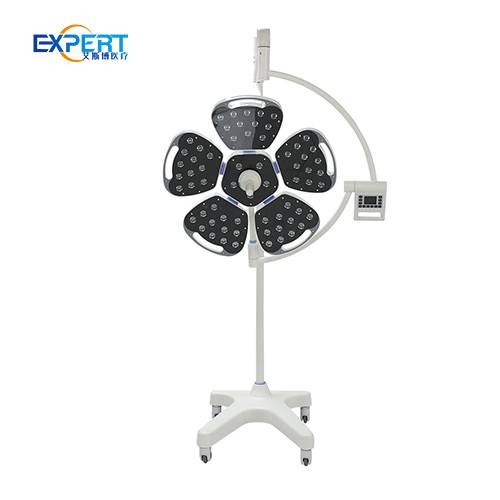
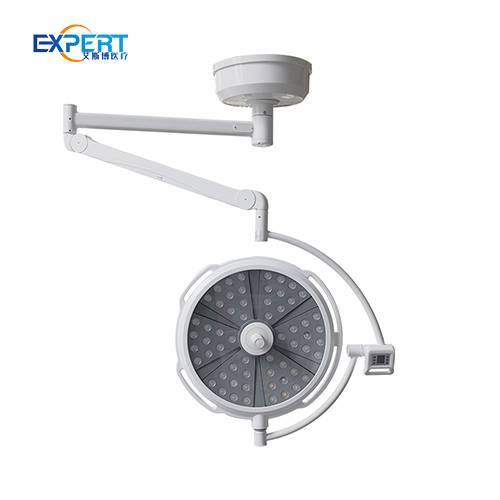
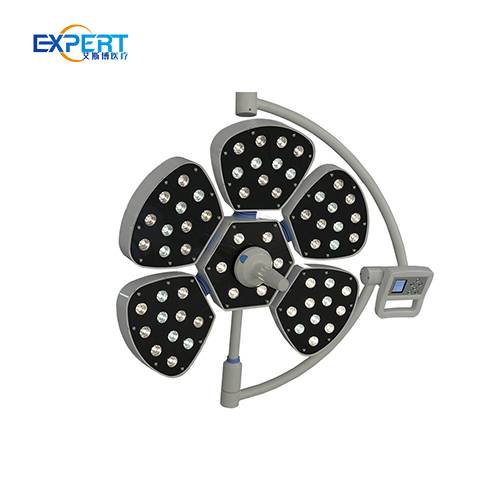
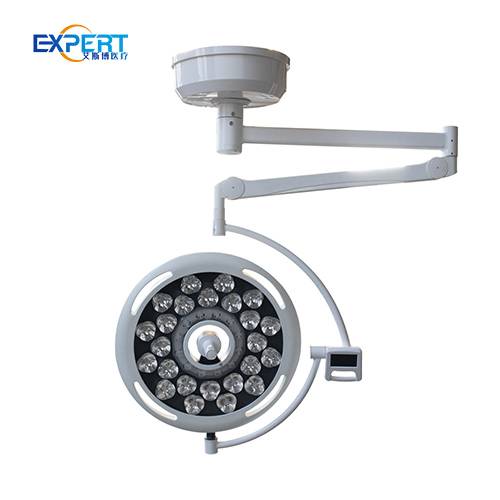








LED surgical lights offer benefits over traditional lighting:
Disadvantages of LEDs include higher upfront costs and slight variations in color consistency between replacements.
Hybrid surgical lights combine multiple lighting technologies into one luminaire. For example, they may use high intensity discharge (HID) lamps along with halogen and/or LED lights.
Benefits of hybrid lights:
Flat panel LED surgical lights are ultra-thin fixtures that provide uniform high intensity illumination.
Advantages include:
Mobile surgical lights are movable floor or ceiling mounted luminaires on wheeled bases. They are optimal to complement main ceiling lights and provide targeted task lighting.
Types of mobile surgical lights include:
Mobile lights help enhance visualization for surgeons by reducing shadows and adjusting to preferable angles. However, they can cause clutter or collisions in smaller operating rooms.

Some important specifications and parameters to evaluate different surgical lighting options include:
| Parameter | Description | Preferred Range |
|---|---|---|
| Illuminance | Amount of light falling on a surface measured in lux or foot candles | 80,000 – 160,000 lux |
| Color Temperature | Warmth or coolness look of the lamp | 3,000 – 6,700 K |
| Color Rendering Index (CRI) | Accuracy of color representation | 90+ |
| Adjustability | Range of motion and positioning | Flexible light heads and articulating arms |
| Field Diameter/Depth | Size of focused light pool | 6 – 12 inches diameter, 20+ inch depth |
| Homogeneity | Evenness of light distribution | > 40% across field |
| Lifetime | Total lamp usage duration | ≥ 30,000 hours preferred |
| Heat Dissipation | Temperature output | Low for LEDs and fluorescents |
| Sterilizability | Ability to sterilize light components | Removable handles preferred |
Fixtures should provide easy positioning, adjustable light intensity, convenient operation for clinicians, and minimal shadowing or glare.
The right surgical lighting improves visibility for intricate work and reduces eye strain for surgeons. Modern LED systems provide bright, uniform, and adjustable illumination that both enhances safety and surgical outcomes. While traditional halogen lamps still have a niche role, innovative flat panels and tunable LED lights better meet the demands of the OR. By selecting surgical luminaries based on intensity, light quality, size, shadow reduction and heat emission, facilities can upgrade both the performance and efficiency of surgery suites. With human lives at stake, investing in the best surgical lighting ultimately supports patient safety during critical procedures.
The main categories of surgical lights are 1) Ceiling-mounted including halogen, LED, hybrid, and flat panel designs 2) Mobile floor or ceiling mounted lights. Within these groups many variations and options exist.
LED ceiling-mounted surgical lights generally provide the best combination of light quality, efficiency, lifetime value and adjustable features. Flat panel LED lights also offer excellent shadow control.
Recommended illuminance levels for surgical lighting are between 80,000 to 160,000 lux across the field. This intense brightness enables visualizations of fine details in body cavities.
Critical parameters surgeons evaluate are color accuracy, field size and depth, uniformity, maneuverability, heat emission, and focal distance from tissue. Choosing lights balances these specifications for optimal visibility of the surgical site.
On average, surgical lighting systems should be replaced every 10-15 years. Though bulbs may keep functioning, older technologies become outdated and replacement parts harder to find. Investing in new energy saving LED systems can deliver rapid ROI.
